Plastic tubing is a tube made from plastic materials used in structural or fluid flow applications or as insulation or sheathing for electrical or heating installations. The plastic tube is a lightweight, adaptable material frequently used in pneumatic, hydraulic, industrial, medicinal, and many other applications as flow lines for fluids and gasses. Read More…
A leading manufacturer and fabricator of flexible plastic tubing and hose, we produce and stock large quantities of a wide variety of materials, including PVC, polyurethane, silicone, nylon and many more.
At Absolute Custom Extrusions, we specialize in plastic tubing, while providing custom plastic extrusions and profiles. Products include distributor tubes, hot or cold water tubes, automotive tubing, medical tubing, shipping tubes and golf club tubes.
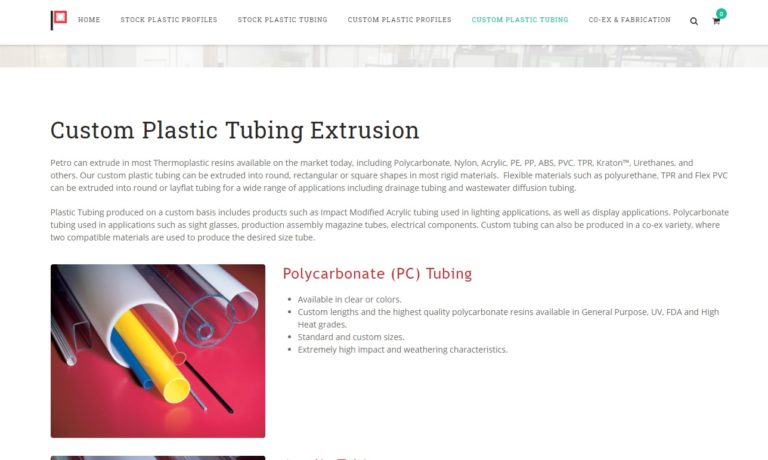
Petro specializes in plastic tubing, offering custom extruded tubing, coiling & angle cutting. Our clear & color plastic tubing is available in Polycarbonate, Acrylic & PE-PP-Nylon.
We are a leading custom extruder of plastic shrink tubing, flexible as well as rigid tubing and profiles. Pexco offers tubing in a wide range of standard and custom colors in a multitude of material options like Polysulfone, PVC, polyurethane, nylon and more. We use state-of-the-art machinery and perform secondary operations on site, such as drilling, slotting, notching, etc. Pexco is ISO 9001...
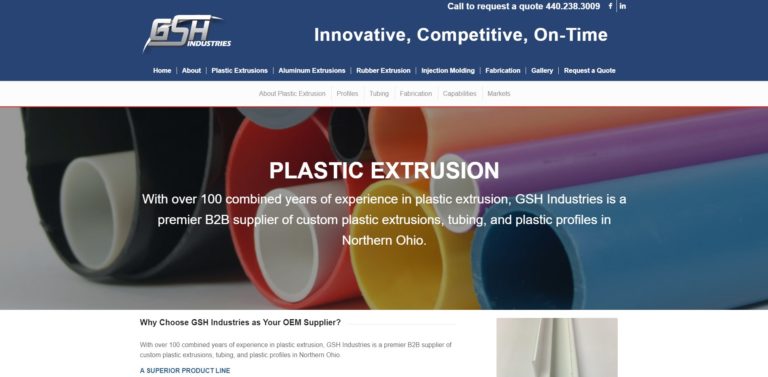
GSH is a manufacturer of plastic, extruded, nylon, polycarbonate and polyethylene tubing. We serve a variety of industries with our products, including automotive, consumer, electrical and marine.
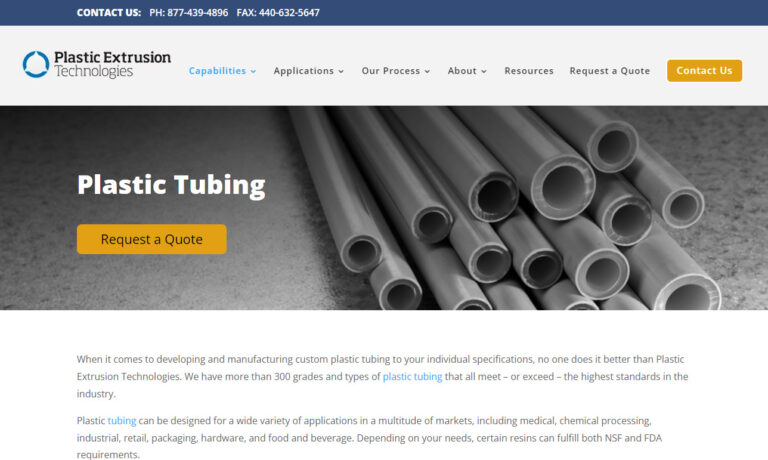
When you choose Plastic Extrusion Technologies, you can rest assured that your custom plastic tubing requirements will be met with precision and excellence. We take pride in being a leader in the custom plastic extrusion industry, consistently striving to exceed your expectations and deliver the solutions you need.
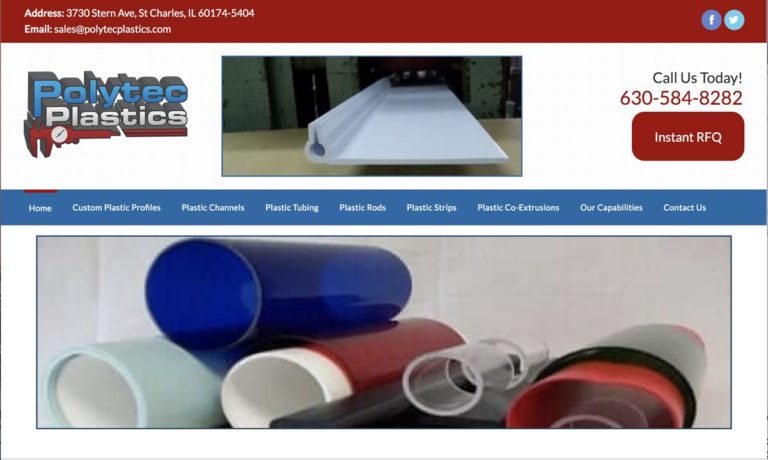
If you are in search of quality plastic tubing then you have found the company that can meet your needs. We have a wide variety of stock plastic tubing items and our solutions are very reliable.
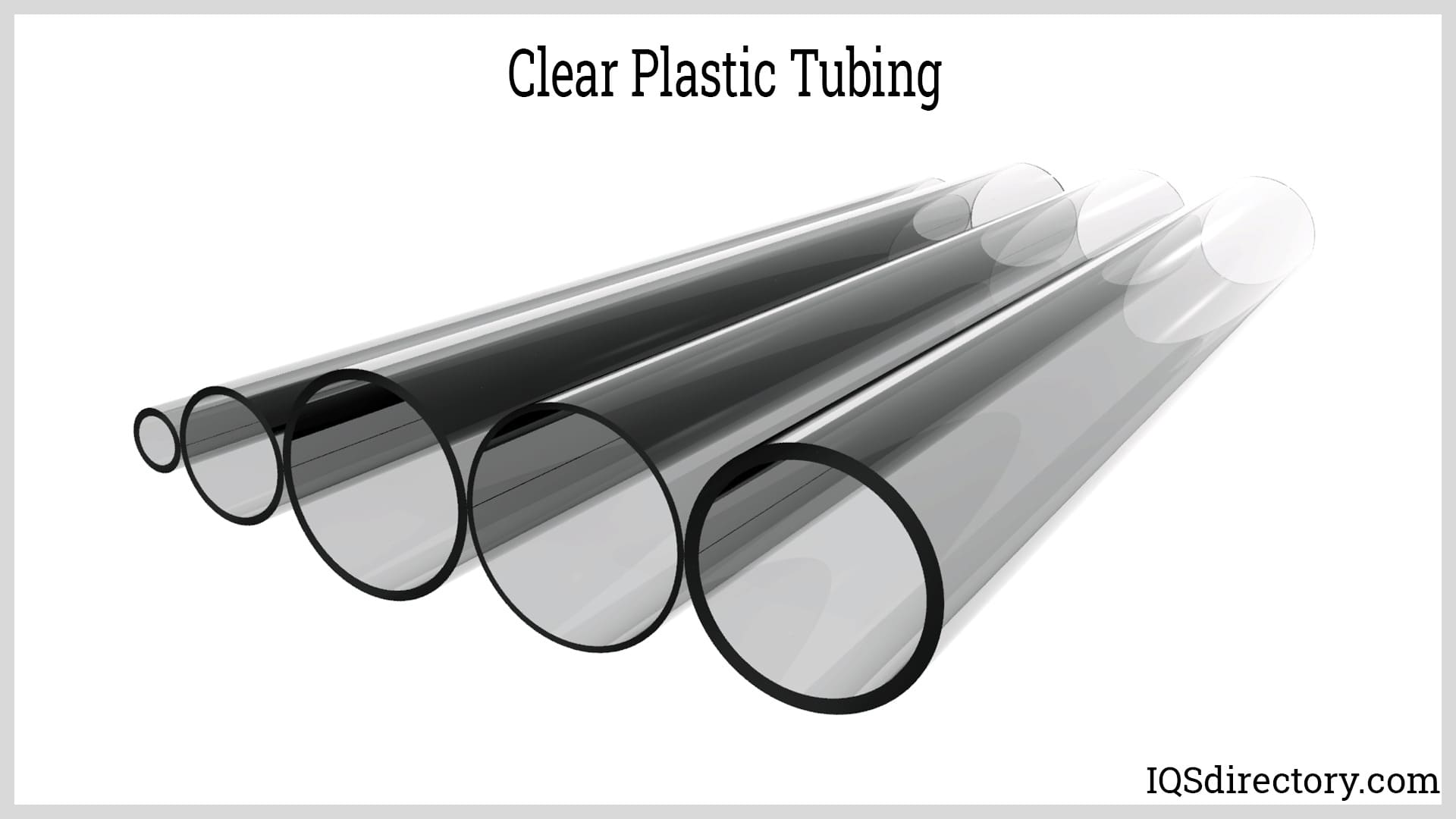
More Clear Plastic Tubing Manufacturers
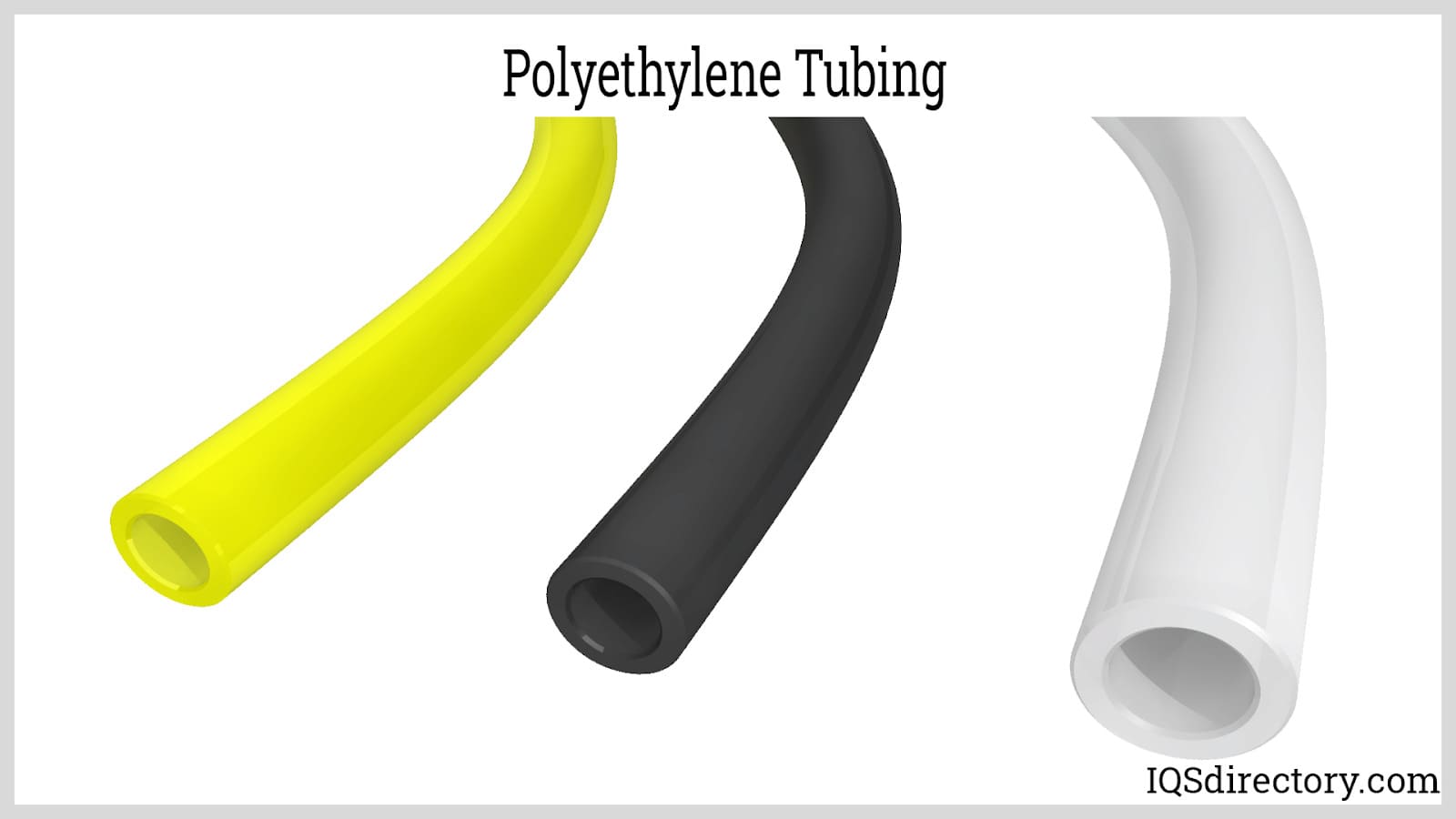
Though the tubing mentioned is often smaller and less rigid than materials classed as hose or pipe, tubing can be flexible or stiff depending on the type of material and its intended use. Products made of clear plastic tubing are hollow, transparent, or semi-transparent tubes used to convey liquids, gasses, and solids (though solids that are moved through tubes are usually granular or free-flowing).

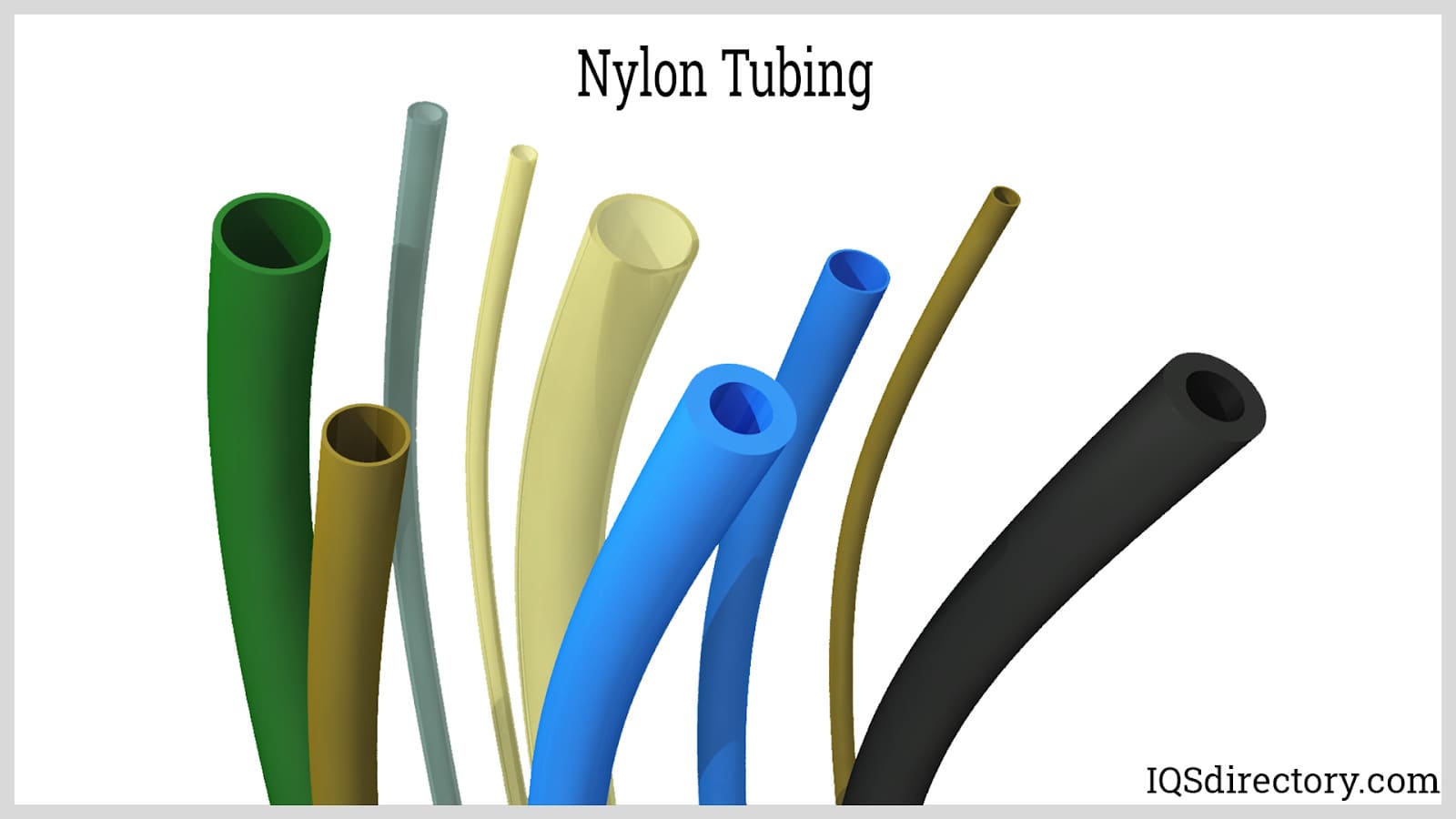
Materials in Clear Plastic Tubing
Nylon, PET, polystyrene, polypropylene, ABS, polyurethanes, and a variety of other basic plastic materials can all be used to make plastic tubing. Many of these materials can also produce clear plastic tubing with proper engineering. However, due to the great degree of transparency they can obtain, acrylic and vinyl are the most often utilized materials to make clear plastic tubing.
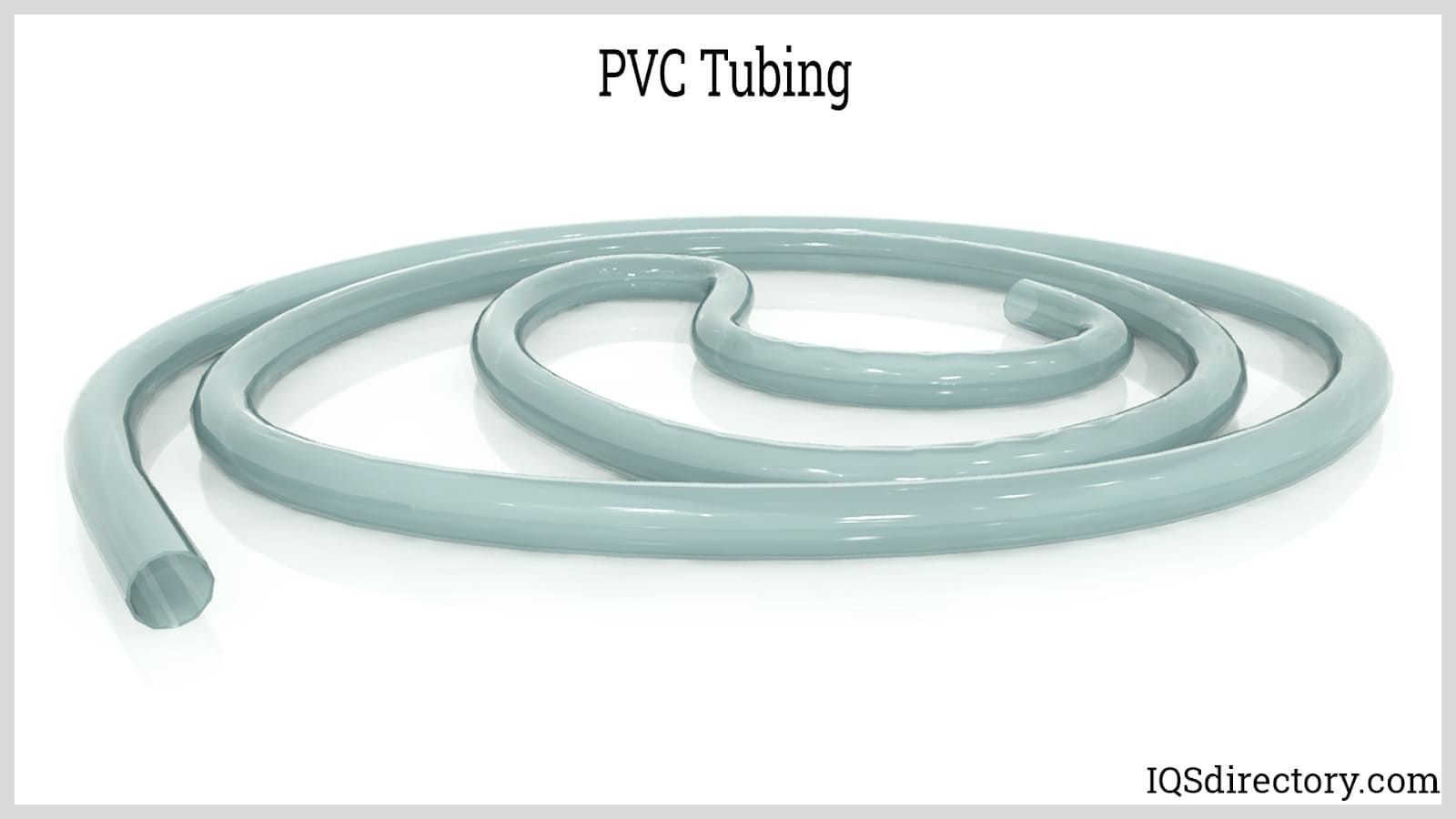
There are numerous processes used to shape raw plastic materials into useful items. But they must first be engineered before they can be created. One of the more readily recognizable types of plastic material is PVC, for instance. However, PVC does not always come in its recognizable opaque, off-white form. Similar to many other plastics that usually have opaque surfaces, it can be designed to be semi-transparent.
Only naturally transparent plastics like acrylic don't need any particular engineering to become transparent. Once the engineering of the raw materials is finished, extrusion is typically used to create the raw materials intended to become plastic tubes.
Manufacturing Process of Clear Plastic Tubing
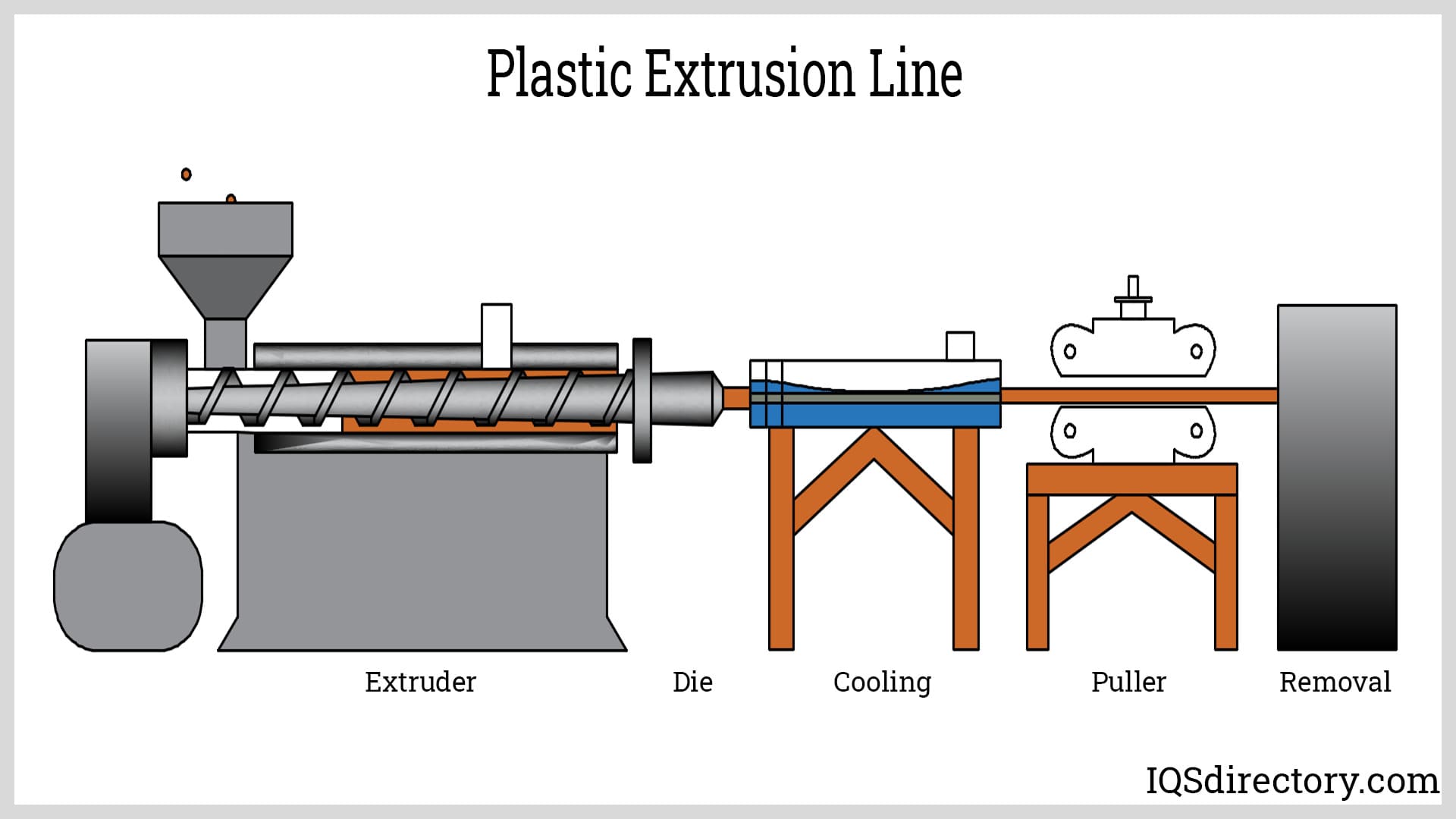
Plastic extrusion is a thermoforming (heat forming) procedure that transforms unfinished plastic materials into useful products. A hopper suspended over a conveyance channel holds a collection of raw plastic (or stock) at the start of the operation. The stock is crushed and heated by a long spinning screw after being lowered into the channel. A die, a device used to shape raw materials, is used to press the stock through after it has been heated until it is molten. The stock is allowed to cool and harden after emerging from the die on the other side in its new tube shape. The new tube is then lengthened and ready for transport or further processing.
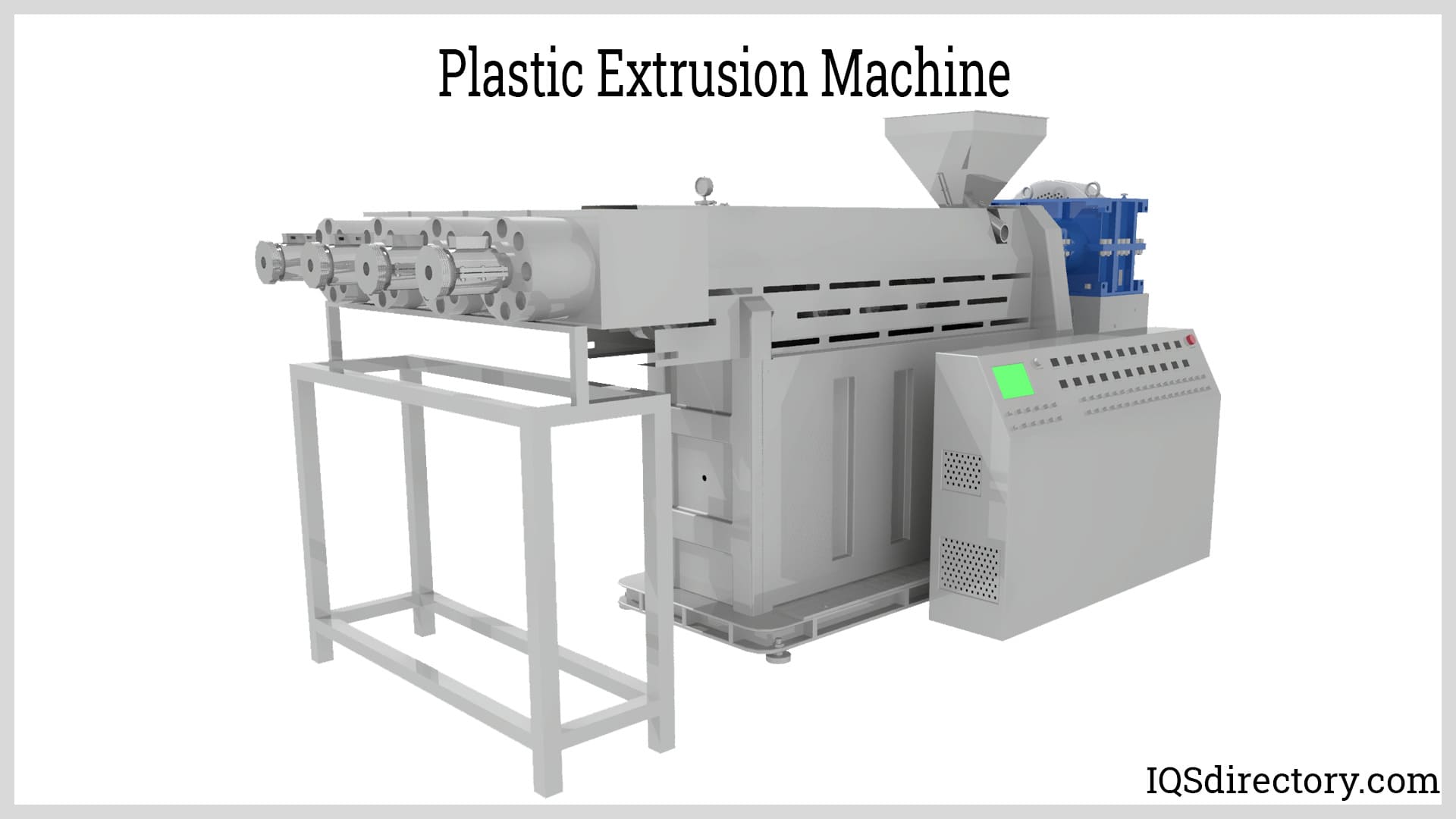
Applications of Clear Plastic Tubing
There are numerous uses for clear tubing. Because many banks offer drive-through services, movable containers and vacuum tubes are needed to convey cash, checks, and receipts from vehicles to interior bank tellers. The shipping tube must be clear because many industries demand that the container being sent be visible inside the tube.
Clear medical tubing is necessary for healthcare settings to measure and monitor the flow of liquids during intravenous medicine administration and the transfer of fluids between apparatus in lab settings. Plastic tubing is widely used in many industries, municipalities, marine settings, automotive products, services sectors, and many other applications.
Benefits of Recycling Clear Plastic Tubing
Properly disposing of single-use items and plastics is one of the numerous difficulties facing any industry, particularly the agricultural sector. The agricultural sector utilizes a lot of plastic, including transparent plastic tubing, compost bags, and various bags for farming goods. Each year, more than 100 million pounds of agricultural waste made of plastic items are dumped in the United States. When this is disposed of in landfills, it significantly impacts the environment and the landfill resources where the plastic must be disposed.
In addition, the facilities must recycle or otherwise dispose of the 20 million pounds of plastic garbage that would otherwise be impossible to keep. Some recycling facilities urge farmers and other agricultural enterprises to recycle plastic tubing and other plastic items to make new plastic goods like bags and containers. This recycling reduces waste and benefits the local landfills and ecosystem. Because many recycling facilities charge for the disposal of plastic waste, many agricultural enterprises have ignored the option to recycle.
Recycling plastic agricultural waste is rare since no farmer wants to pay money to recycle when they have already paid for trash removal services. However, a few businesses have done away with the cost of recycling plastic. This free or reduced-cost service helps the farmers by giving them a place to dispose of their waste materials, which improves both the environment and their wallets.
The environment will benefit more from this method if more recycling facilities adopt it. As a result, there won't be as many products requiring new plastic, there won't be as much waste in landfills, and farmers will save more money. This triple win is advantageous to numerous global sectors.

Choosing the Correct Clear Plastic Tubing Supplier
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing clear plastic tubing from a clear plastic tubing supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of clear plastic tubing suppliers. Each clear plastic tubing supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each clear plastic tubing business website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple clear plastic tubing companies with the same form.






 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators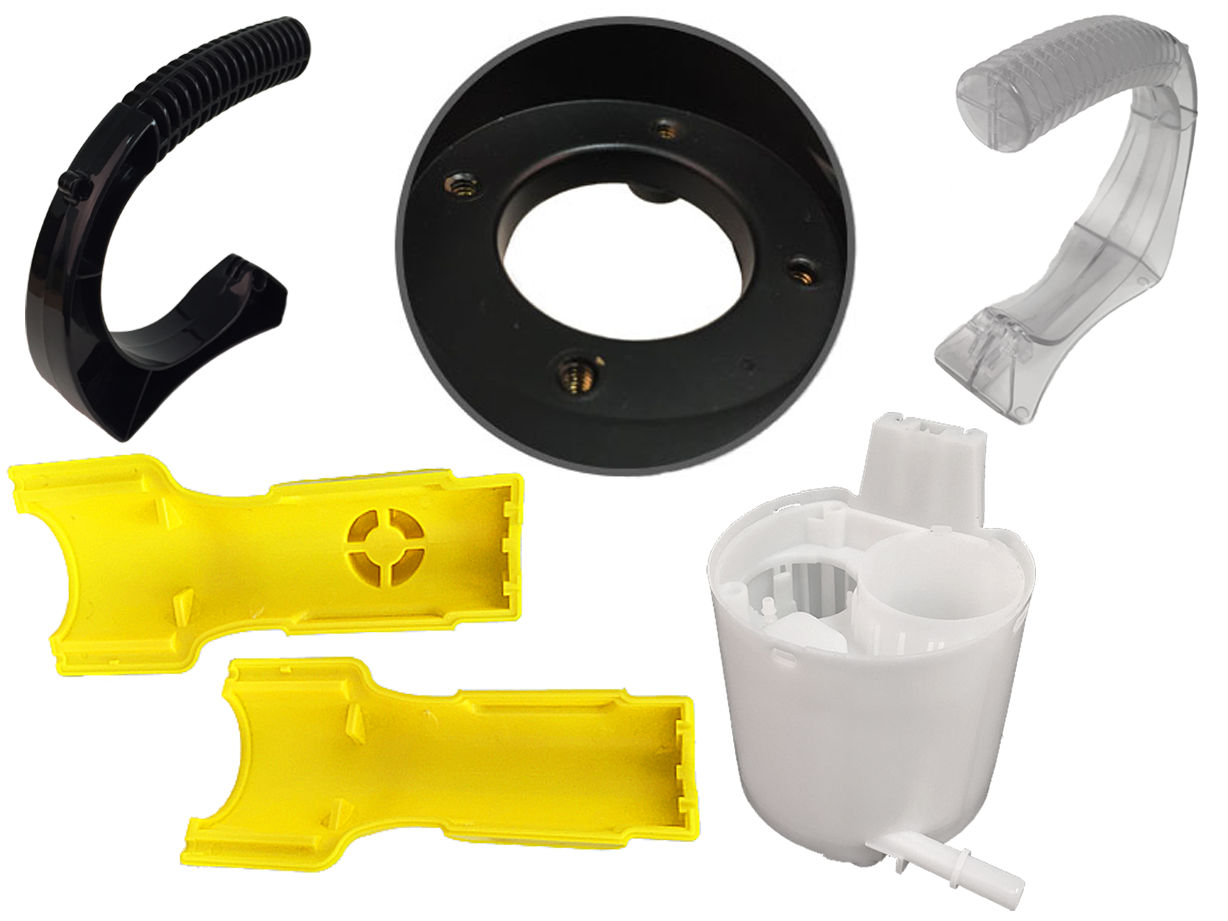 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics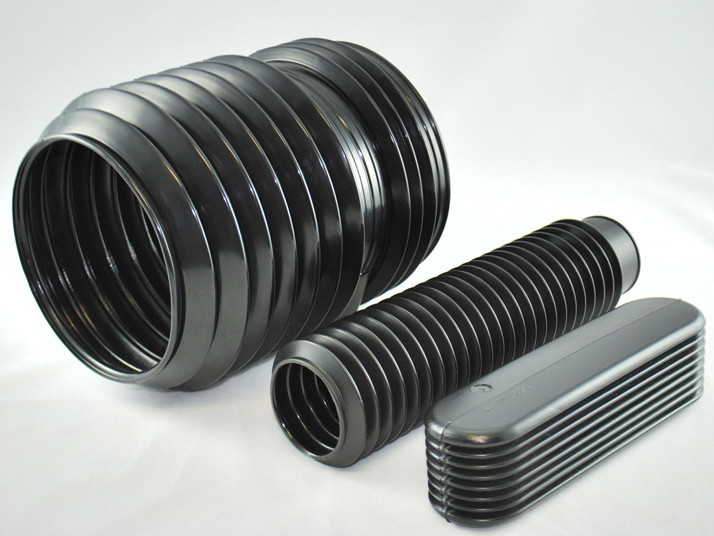 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding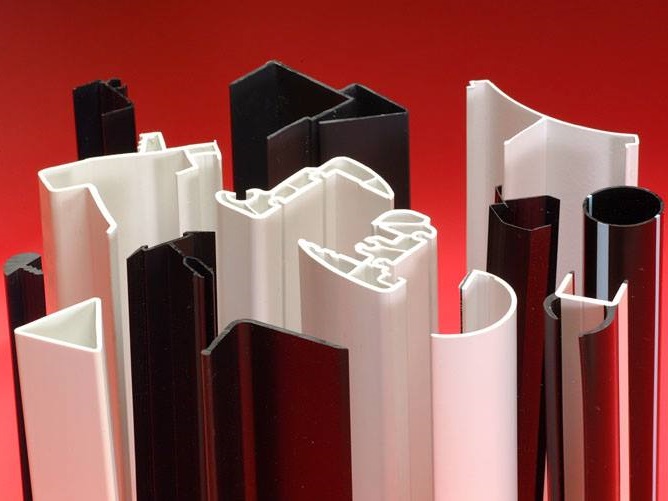 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding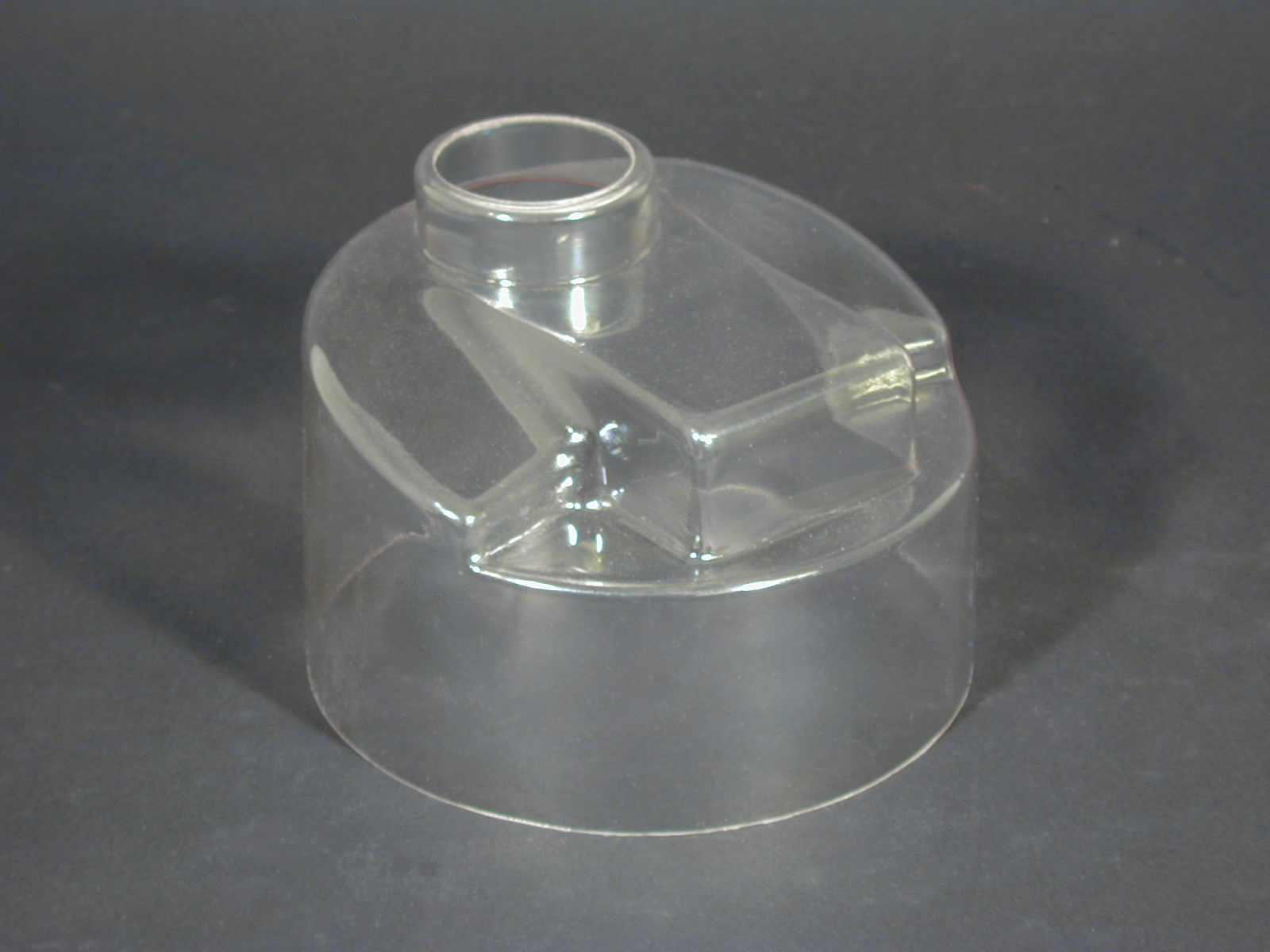 Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services